Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar elements crucial in many modern technologies. Among these, Terbium (Tb) and Europium (Eu) stand out for their significant roles in the electronics and energy sectors. This article compares and contrasts Terbium and Europium, exploring their properties, applications, and economic importance.
Properties:
http://images-of-elements.com/, CC BY 1.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Common Uses:
Significance: Terbium's ability to produce bright green light and enhance magnetic materials makes it indispensable in the electronics and renewable energy industries. Its role in creating energy-efficient lighting solutions contributes to sustainability efforts globally.
Properties:
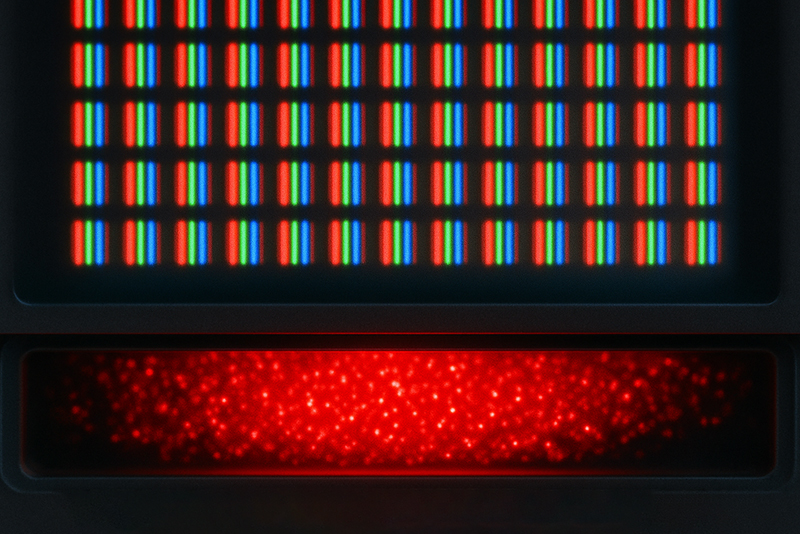
Jurii, CC BY 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Common Uses:
Significance: Europium's unique red and blue emissions are critical for the vivid colors in modern display technologies. Its use in nuclear reactors and security features for currency highlights its diverse applications beyond consumer electronics.
Terbium:
Europium:
Terbium:
Europium:
Terbium:
Europium:
Terbium:
Europium:
Terbium and Europium, two vital rare earth elements, play crucial roles in modern technology. Terbium's contribution to magnets and lighting, along with Europium's importance in displays and nuclear reactors, underscore their unique properties and applications. As the demand for advanced technology and sustainable solutions grows, the significance of these elements in our daily lives and future innovations cannot be overstated. The continued exploration and responsible management of Terbium and Europium resources are essential to support technological progress and environmental sustainability.
Organizations like Stanford Materials Corporation (SMC) play a critical role in supplying these rare earth elements, ensuring that industries worldwide can access the materials they need for innovation and growth. SMC's commitment to quality and sustainability helps bridge the gap between resource availability and technological advancement, driving progress in various high-tech and green sectors.
Eric Loewen
Eric Loewen graduated from the University of Illinois studying applied chemistry. His educational background gives him a broad base from which to approach many topics. He has been working with topics about advanced materials for over 5 years at Stanford Materials Corporation (SMC). His main purpose in writing these articles is to provide a free, yet quality resource for readers. He welcomes feedback on typos, errors, or differences in opinion that readers come across.

 Inquiry List
Inquiry List