- Catalog No.TM0099
- MaterialTitanium
Titanium and Titanium alloys can be used in aerospace, military, medical, jewelry, telecommunications and other industries.
Titanium and Titanium alloys can be used in aerospace, military, medical, jewelry, telecommunications and other industries.


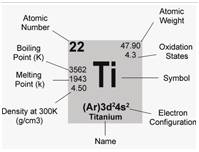
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and an atomic number of 22. Compared to other metals, it is a lustrous and silver transition metal with low density and high corrosion resistance to seawater, aqua regia and chlorine, etc.
Titanium and Titanium alloys can be used in aerospace, military, medical, jewelry, telecommunications and other industries.
There are several grades of Titanium. Grade 1 to Grade 4 are pure Titanium, and the other grades are of alloys. Pure Titanium is used for its high corrosion resistance, and its alloys, for their extremely high strength-to-weight ratio.
Stanford Materials, founded in 1994, focuses on supplying high-quality Titanium products to worldwide customers at competitive prices. We provide a variety of commercially pure Titanium (CP Titanium) and Titanium alloys in a ball, wire, sheet, bar, pipe, tube, and other forms. We also provide Titanium sponge, Titanium powder and Titanium machining components.
Titanium history
Titanium was discovered by amateur geologist William Gregor. Four years later, German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth independently discovered the new element in rutile and named it after the Titans of Greek mythology.
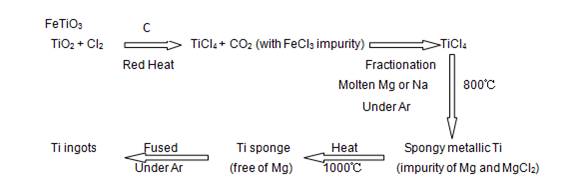
Pure metallic Titanium (99.9%) was first obtained in 1910 by Matthew A. Hunter at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute by heating the mixture of TiCl4 and Sodium at 700-800?C. In 1932 William Justin Kroll proved that Titanium metal could be produced by reducing Titanium Tetrachloride (TiCl4) with Calcium. Eight years later he refined this process by using Magnesium and even Sodium, which was known later as the Kroll process.
Kroll process
Standards for Titanium products
ASTM F: a standard for medical products
ASTM B: is a standard for industrial products
AMS & MIL: a standard for aerospace and military products
Titanium materials' grades
» Titanium materials of grade 1-4 are unalloyed and considered commercially as pure or "C.P.". Generally speaking the tensile and yield strength goes up with the number of these grades.
» Those of grade 5, also known as Ti6Al4V, Ti-6Al-4V or Ti 6-4, is the most commonly used alloys because of their special physical and chemical properties. they have a chemical composition of 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium, 0.25% (maximum) Iron, 0.2% (maximum) Oxygen and the rest is Titanium.
» Those of grade 7 contain 0.12% to 0.25% Palladium. The small amount of Palladium gives them improved crevice corrosion resistance at low temperatures and high pH.
» Those of grade 9 contain 3.0% Aluminum and 2.5% Vanadium. They are often used in aircraft tubing for hydraulics and in athletic equipment.
» Those of grade 12 contain 0.3% Molybdenum and 0.8% Nickel.
» Those of grade 23 contain 6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium, and 0.13% (maximum) Oxygen.
Chemical components of each grade
|
Grade |
Fe% |
C% |
N% |
H% |
O% |
Al% |
V% |
Mo% |
Ni% |
Pd% |
Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gr1 |
0.2 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.18 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL. |
|
Gr2 |
0.3 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.25 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL. |
|
Gr3 |
0.3 |
0.08 |
0.05 |
0.015 |
0.35 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL. |
|
Gr4 |
0.3 |
0.08 |
0.05 |
0.015 |
0.40 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL |
|
Gr5 |
0.25 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.02 |
5.5 - 6.75 |
3.5 - 4.5 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL |
|
Gr7 |
0.3 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.25 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
0.12 - 0.25 |
BAL. |
|
Gr9 |
0.25 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.15 |
2.5 - 3.3 |
2.0 - 3.0 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL. |
|
Gr12 |
0.3 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.25 |
-- |
-- |
0.2 - 0.4 |
0.6 - 0.9 |
-- |
BAL. |
|
Gr23 |
0.3 |
0.08 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.13 |
5.5 - 6.75 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
BAL |
Mechanical characteristics of each grade
|
Grade |
Tensile Strength (min) |
Yield Strength 0.2% Offset |
Elongation in 2 inch or 50mm % (min) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
KSI |
MPa |
KSI |
MPa |
||
|
Gr.1 |
35 |
240 |
20 - 45 |
138 - 310 |
24 |
|
Gr.2 |
50 |
345 |
40 - 65 |
275 - 450 |
20 |
|
Gr.3 |
65 |
450 |
55 - 80 |
380 - 550 |
18 |
|
Gr.4 |
80 |
550 |
≥70 |
≥483 |
15 |
|
Gr.5 |
138 |
950 |
≥128 |
≥880 |
14 |
|
Gr.7 |
50 |
345 |
≥40 |
≥275 |
24 |
|
Gr.9 |
125 |
860 |
≥105 |
≥725 |
10 |
|
Gr.12 |
70 |
483 |
≥50 |
≥345 |
18 |
|
Gr.23 |
125 |
860 |
≥115 |
≥790 |
15 |

 Inquiry List
Inquiry List